Capacitors are widely used in electric circuits to store energy, suppress voltage spikes, and filter noise, ultimately enhancing a product's performance. Although capacitors consist of conductors and a dielectric material, configurations and characteristics vary. Selecting a capacitor with the appropriate specifications will ensure it optimally and safely powers your design.
Different Types of Capacitors
Many types of capacitors exist to suit different applications. Here are some of the most prevalent types of capacitors:
Non-Polarized Capacitors
Examples of non-polarized capacitors include:
- Film capacitors: These capacitors feature a dielectric layer composed of various polymer types. Metallized polyester film capacitors offer self-healing capabilities, which are superior for high-pulse and voltage-reversal applications. Compared to other capacitors, film capacitors have low ESR and ESL.
- Ceramic capacitors: This capacitor type features a ceramic dielectric material and is economical, versatile, and available in various voltage and capacitance ranges. These capacitors can offer low losses and high stability, making them suitable for resonant circuit and decoupling applications. Multilayer ceramic capacitors consist of numerous dielectric layers, enabling increased capacitance. Ceramic capacitors have no polarization requirement and are ideal for applications with high voltages, pulse loads, and frequencies.
Polarized Capacitors
Standard polarized capacitors include:
- Electrolytic capacitors: Two common subtypes of electrolytic capacitors include tantalum and aluminum. A tantalum capacitor comprises tantalum metal and a thin oxide dielectric layer and is often used to filter the power supply in electronics with precise size constraints. An aluminum capacitor is made of aluminum and a thin aluminum oxide dielectric layer, offering large capacitance for its size.
- Conductive polymer capacitors: Another subtype of electrolytic capacitors, conductive polymer capacitors, uses a solid electroconductive polymer as an electrode. Since it does not use liquid electrolytes, it will not dry out, offering a long life. These capacitors also provide low ESR, excellent stability, and a high operating temperature range. Their low ESR makes them suitable for applications with high ripple current.
Core Factors to Consider in Capacitor Selection
Before selecting a capacitor, it's important to understand your application's requirements. Keeping your application's constraints in mind will help you select a capacitor that matches your design. A custom option may be the best choice depending on your unique needs.
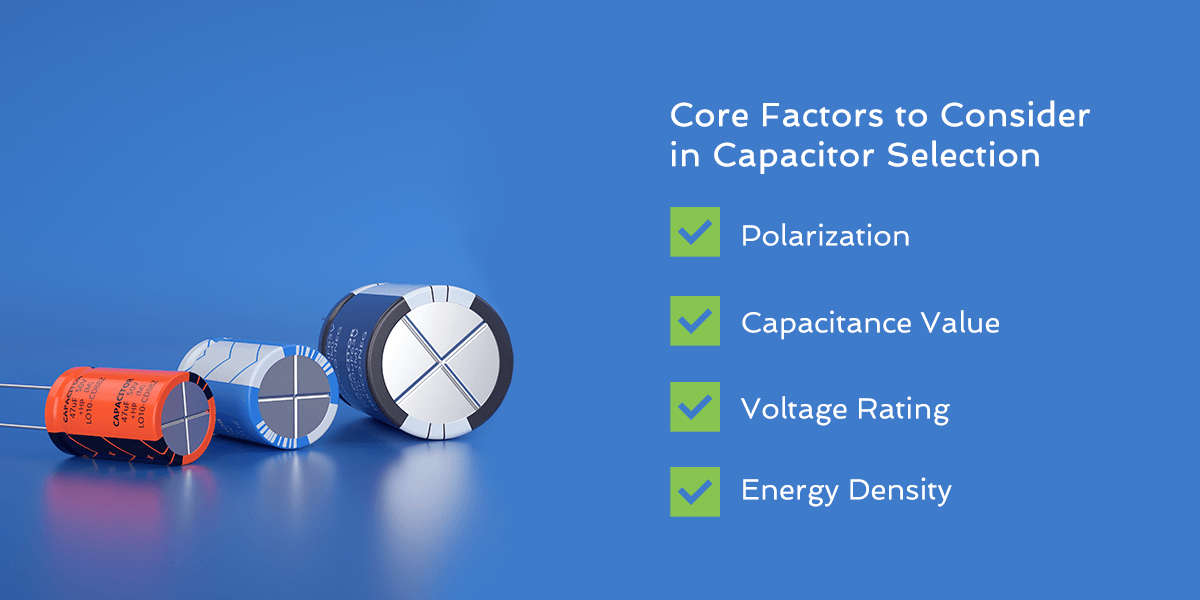
Generally, you will want to assess polarization, capacitance, voltage, and energy density as the core considerations for capacitor selection.
Polarization
The most important factor to keep in mind is polarization; whether you require a polarized or non-polarized capacitor will drastically narrow down your options. Each category of capacitor is available in different designs and materials and provides either lower or higher capacitance values. Establish the need for polarization first before moving on to other considerations.
Capacitance Value
This value describes a capacitor's ability to store an electrical charge at a particular voltage level. Capacitance is measured in farads, with 1 farad (F) equaling one unit of capacitance. Since a farad is typically much more capacitance than needed, capacitance is often expressed in microfarads (μF), where 1 μF equals one-millionth of a farad. Greater μF may be suitable for energy-storage or filtering applications, depending on your circuit's requirements.
Voltage Rating
Voltage rating is the highest voltage at which the capacitor can operate safely. It is recommended to select a capacitor with a voltage rating higher than your circuit requires. For example, if your circuit demands 24 volts, choose a capacitor with a voltage rating above 24 volts.
Energy Density
Energy density is the amount of energy a capacitor stores per unit of volume. It's typically expressed as watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg) or per liter (Wh/L). A capacitor with higher Wh/L than another option of the same size has a greater ability to store energy and can potentially supply electrical power longer.
Additional Factors to Consider in Capacitor Selection
Considering the following factors will further assist you in selecting the ideal capacitor for your application:
ESR
Equivalent series resistance (ESR) describes a capacitor's internal resistance. Internal resistance generates heat and leads to energy loss, so it is generally best to choose a capacitor with a low ESR. The ESR may not be specified in a capacitor's datasheet but expressed through other parameters, such as dissipation factor.
ESL
Electric series impedance (ESL) refers to how the capacitor affects the flow of alternating current in terms of total opposition. When considering ESL, you will want to note operation frequency, power-supply stability, and more specific factors like filtering and decoupling to choose a suitable capacitor.
Operating Temperature Range
This describes the temperature limits at which the capacitor can operate safely and effectively. Consider your circuit's operating temperature range and operating environment conditions to choose a capacitor that will function optimally.
Dielectric Material
Dielectric material directly impacts the capacitance value. Dielectric materials have varying levels of permittivity, or ability to store energy in an electric field. For example, barium titanate, a component in ceramic capacitors, has higher permittivity, leading to higher capacitance. Also, the dielectric material's cycle life and loss should be considered because they impact capacitor longevity and performance.
Size and Form Factor
In some cases, you may need to consider size and form factor. These aspects determine how well the capacitor will fit your circuit's dimensions and whether it meets your mounting requirements. Capacitors typically feature surface-mount or through-hole designs. Through-hole capacitors have leads designed to be inserted through PCB holes and soldered into place. They are available in radial or axial arrangements. Surface-mount capacitors attach directly to the surface of the PCB.
Industry Standards
If possible, select capacitors that comply with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment (RoHS) standards. RoHS restricts using hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium. Look for capacitors that established safety agencies recognize to ensure product quality.
Supplier Reputation
A dependable capacitor supplier will help you complete your design faster and with greater peace of mind. At Tecate Group, we are committed to providing high-quality capacitors and custom solutions with fast turnarounds. We also maintain certification with ISO 9001:2015, assuring our commitment to quality and partner satisfaction.
Capacitors for Specific Applications
Although capacitors are generally versatile, certain types are better suited for specific applications. Here are a few common applications and their corresponding capacitors:
- Power-supply filtering: Electrolytic capacitors, such as aluminum capacitors, effectively filter noise due to high capacitance values.
- Coupling or decoupling: Ceramic capacitors are suitable for coupling or decoupling applications in various circuit types because they perform well in high-frequency and high-voltage applications. They are also compact and available in various capacitance values, allowing flexibility in coupling or decoupling.
- Bypassing: Ceramic capacitors are well suited for bypassing applications because they can perform at high frequencies. Aluminum or tantalum capacitors are also suitable for bypassing in low-frequency applications due to their high capacitance values and compactness.
- Snubber circuits: Film capacitors are suitable for snubber circuits due to their low ESR and self-healing characteristics, enabling them to offer reliability in high-voltage applications.
Why Trust Us?
Tecate Group has over 40 years of experience manufacturing and supplying electronic components. Our experience includes serving the industrial-equipment, data-storage, telecommunications, and transportation industries, as well as other industries that rely on capacitors to achieve high-performing electrical systems.
Our dedication to solving our customers' problems sets us apart. Whether you need assistance matching a capacitor to your product's specifications or require a custom design, you can count on our experienced engineers to offer a reliable solution.
Contact Tecate for Expert Guidance
If you need help selecting the appropriate capacitor for your product's design, our team is ready to assist with capacitors that are designed and manufactured to your exact specifications. Along with providing quality standard capacitor options, we can create a custom design based on factors like your voltage and sizing needs.
Our solutions undergo rigorous testing to ensure quality, safety, and reliability. Contact us today to learn more about our standard capacitors or custom solutions.